Introduction
As we embark on Day 62 of our journey, we delve into the powerful combination of Terraform and Docker. Today's focus is on understanding the theory behind leveraging Terraform for the automated provisioning and management of Docker containers.
Provider Configuration
What is a Provider?
In Terraform, a provider is a plugin that facilitates the interaction between Terraform and a specific service or technology. For Docker, we use the docker provider, and we configure it within a provider block:
terraform {
required_providers {
docker = {
source = "kreuzwerker/docker"
version = "~> 2.21.0"
}
}
}
provider "docker" {}

Here, the required_providers block informs Terraform about the provider to be used—docker in this case—along with its source (the provider's namespace on the Terraform registry) and version.
Docker Provider Configuration
The provider "docker" {} block configures the Docker provider, establishing a connection between Terraform and Docker. This connection allows Terraform to manage Docker resources seamlessly.
Resource Blocks
Docker Image Resource
resource "docker_image" "nginx" {
name = "nginx:latest"
keep_locally = false
}
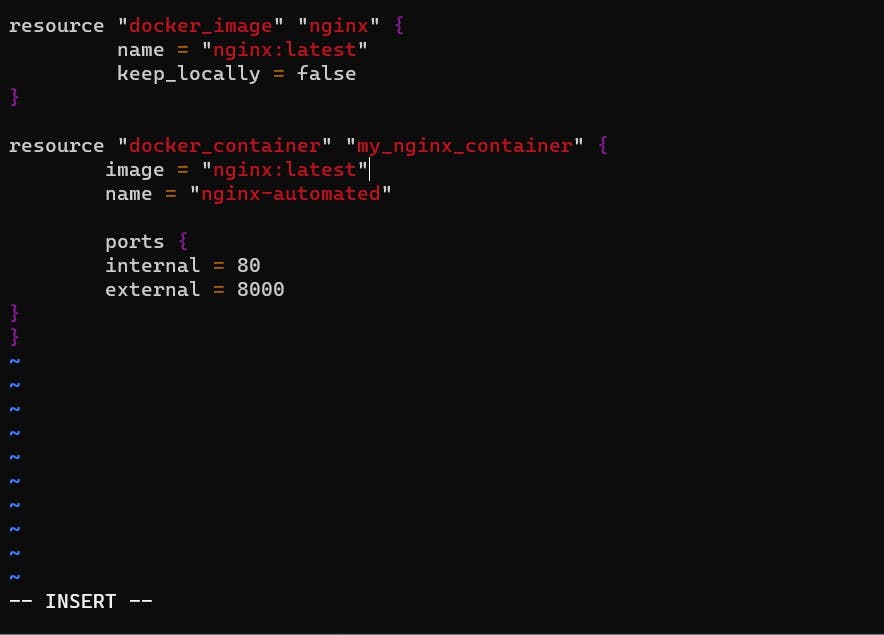
Understanding the Docker Image Resource
In Terraform, a resource represents a tangible part of your infrastructure. The docker_image resource block, named "nginx," defines the parameters for a Docker image. Here, we specify the image name ("nginx:latest") and whether to keep the image locally.
Docker Container Resource
resource "docker_container" "nginx" {
image = docker_image.nginx.latest
name = "tutorial"
ports {
internal = 80
external = 80
}
}
Understanding the Docker Container Resource
The docker_container resource block creates and manages Docker containers. It references the previously defined Docker image ("nginx:latest") and sets up the container with a name ("tutorial") and port mapping.
Task Completion
With these resource blocks, we've effectively instructed Terraform on managing Docker resources for us. Let's go through the remaining steps:
terraform init
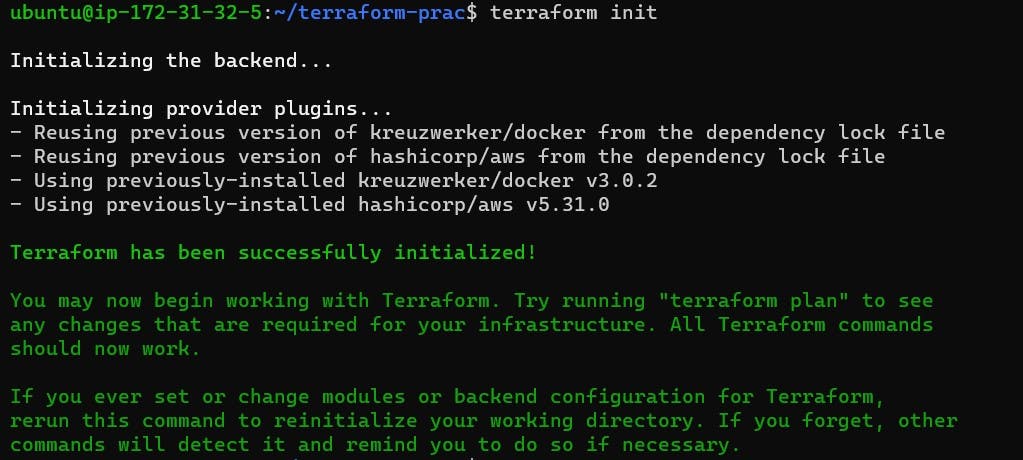
The terraform init command initializes the working directory, downloading the necessary provider plugins, and preparing the environment for Terraform.
terraform validate

The terraform validate command checks the current directory for syntax errors and validates the configuration files.
terraform plan

The terraform plan command generates an execution plan, detailing what actions Terraform will take to apply the desired state. Review this plan to ensure it aligns with your expectations.
terraform apply

Finally, the terraform apply command executes the plan, creating or updating the Docker resources as specified in the Terraform configuration.
Now, Terraform will orchestrate the deployment, pulling the specified Docker image, creating a container based on our defined parameters, and applying any other changes we've configured.

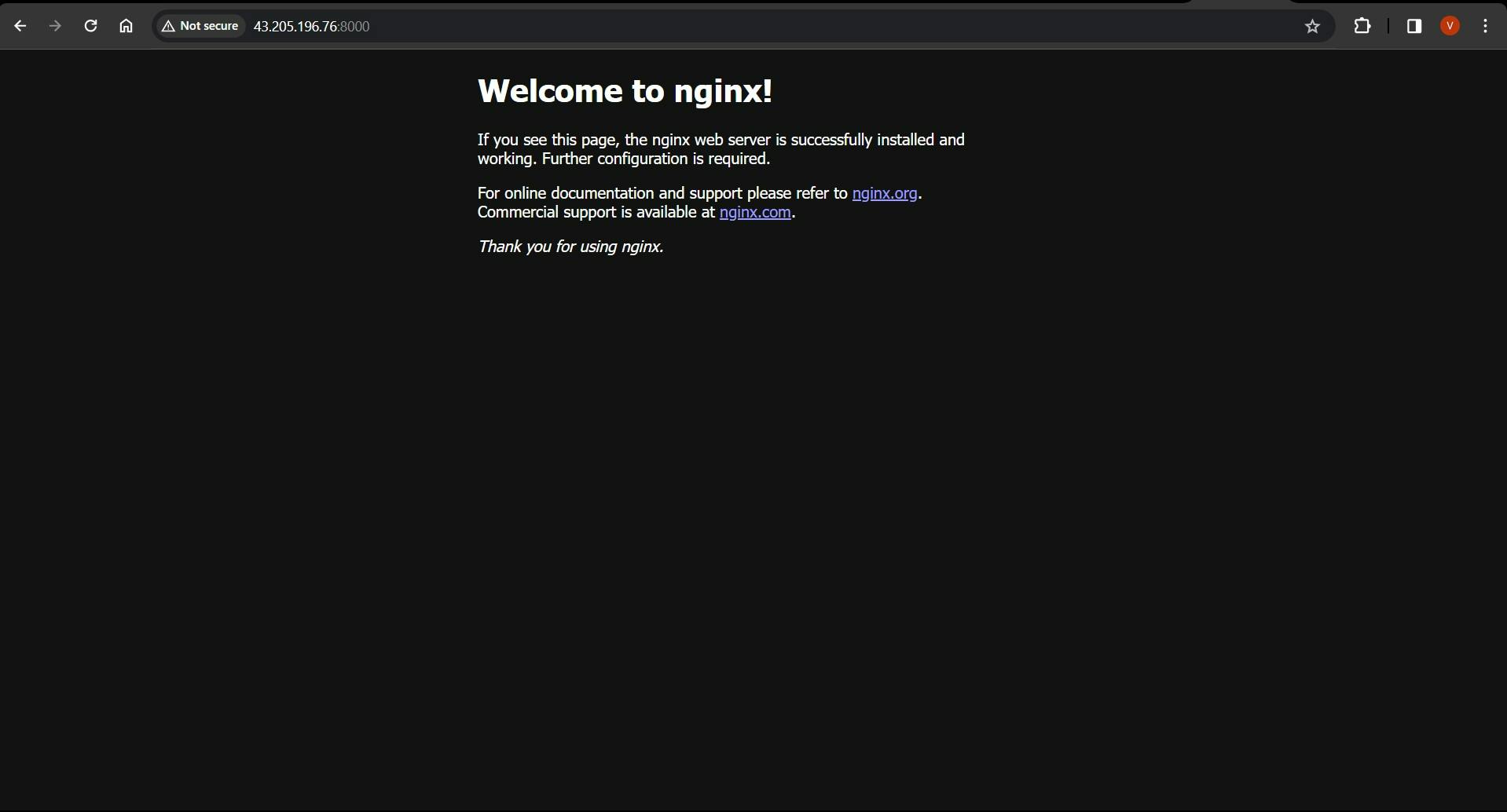
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of Terraform and Docker empowers us to automate the deployment and scaling of containerized applications. By understanding the theory behind these tools and following the Terraform workflow, we unlock a world of possibilities for efficient infrastructure management.
Stay tuned for more exciting adventures with Terraform and Docker!