Day 83: Project 4- Deploying a Web App with Docker Swarm on AWS: Step-by-Step Implementation"
Introduction: In Project 4, we embark on the journey of deploying a web application using Docker Swarm on AWS. Follow along as we set up a robust and scalable environment for hosting applications, walking through each step meticulously.
Step 1: Setting Up AWS Instances Begin by navigating to the AWS portal and creating three new instances named Swarm-manager, Swarm-worker1, and Swarm-worker2.

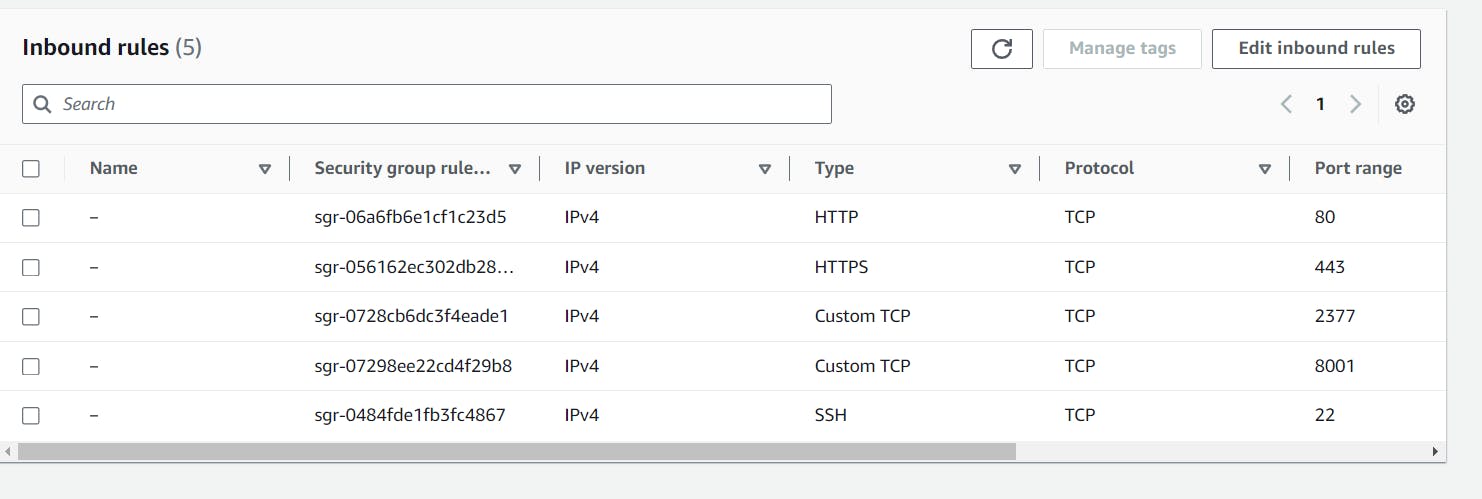
Step 2: Configure Inbound Rules Within the AWS console, ensure that the inbound rules for all instances allow Custom TCP traffic on ports 2377 and 8001 from anywhere (IPv4).
Step 3: Installing Docker Engine On each of the instances, proceed to install Docker Engine. You can refer to other articles or guides for detailed instructions on Docker Engine installation.
https://veddevopsblog.hashnode.dev/day-16-exploring-docker-a-devops-journey
Step 4: Initializing Docker Swarm Log into the Swarm-manager node and initialize Docker Swarm by executing the command: "sudo docker swarm init". This command initializes an empty Docker Swarm.
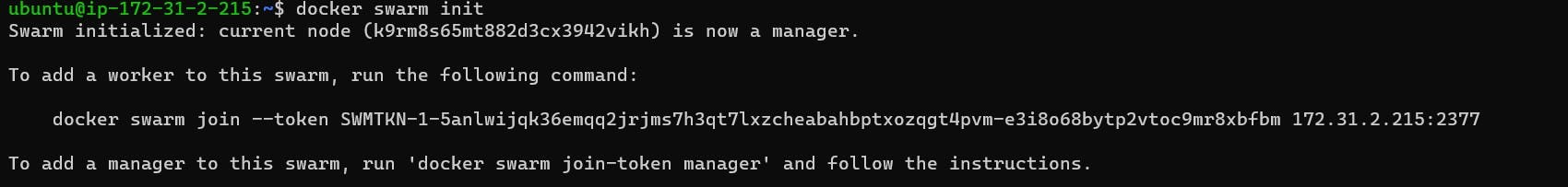
Step 5: Adding Worker Nodes Upon initializing the swarm, a key will be generated. Copy this key and execute it on the Swarm-worker1 and Swarm-worker2 nodes to add them as worker nodes to the swarm.


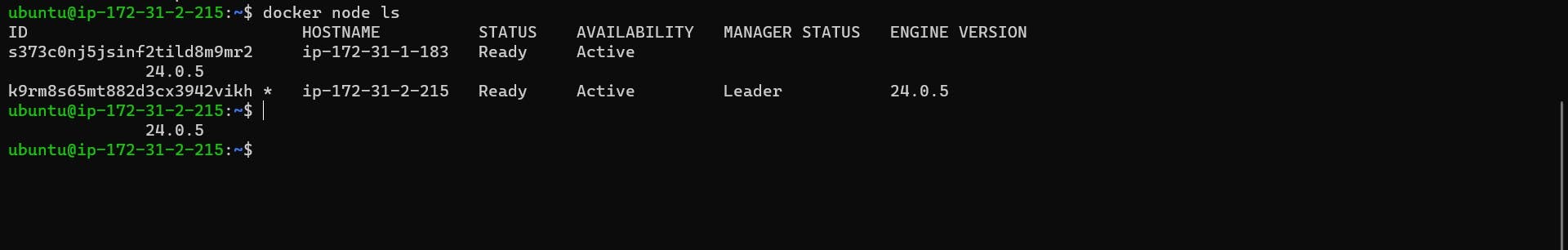
Step 6: Verifying Swarm Nodes To ensure all nodes are properly added, run the command "docker swarm node ls" on the Swarm-manager node to list all nodes within the swarm.
Step 7: Creating a Docker Service On the Swarm-manager node, create a Docker service by running the following command: "sudo docker service create --name django-app-service --replicas 3 --publish 8001:8001 trainwithshubham/react-django-app:latest".

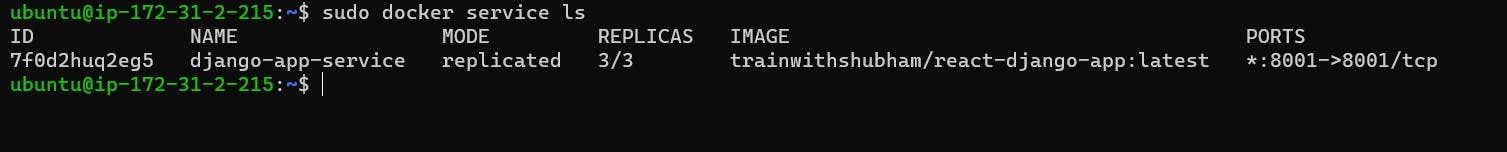
Step 8: Listing Docker Services Check the status of Docker services within the swarm by executing "sudo docker service ls" on the Swarm-manager node.
Step 9: Checking Running Containers To verify that the service has successfully created containers across the nodes, execute "sudo docker ps" on any node within the swarm.

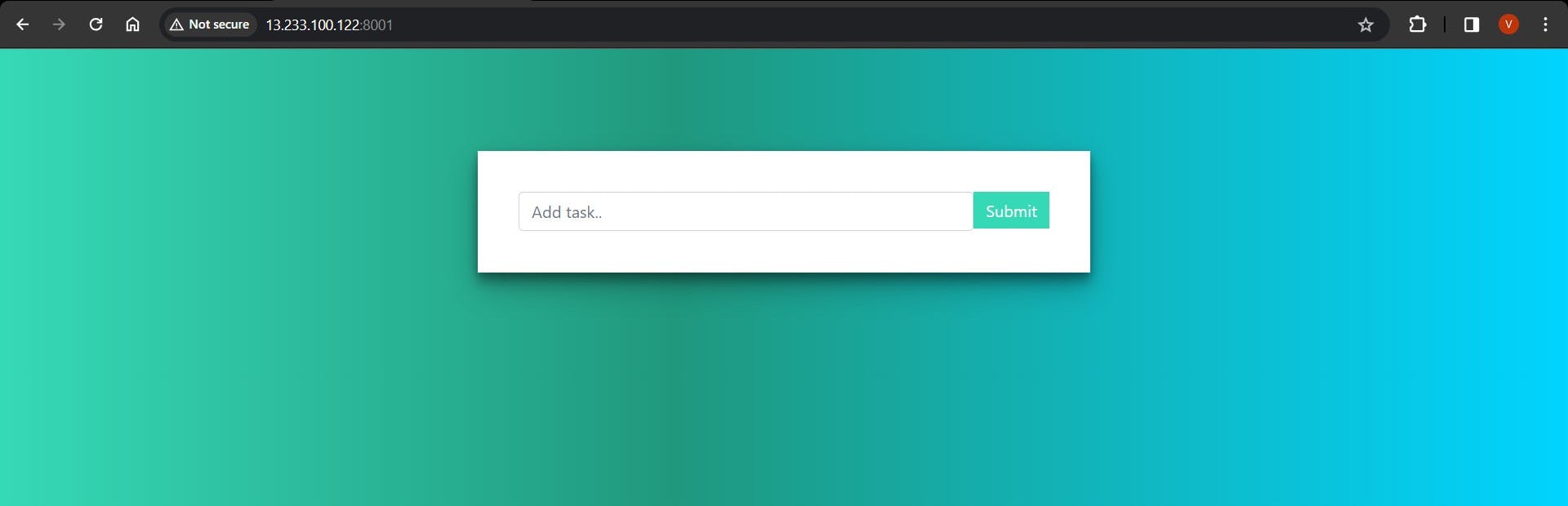
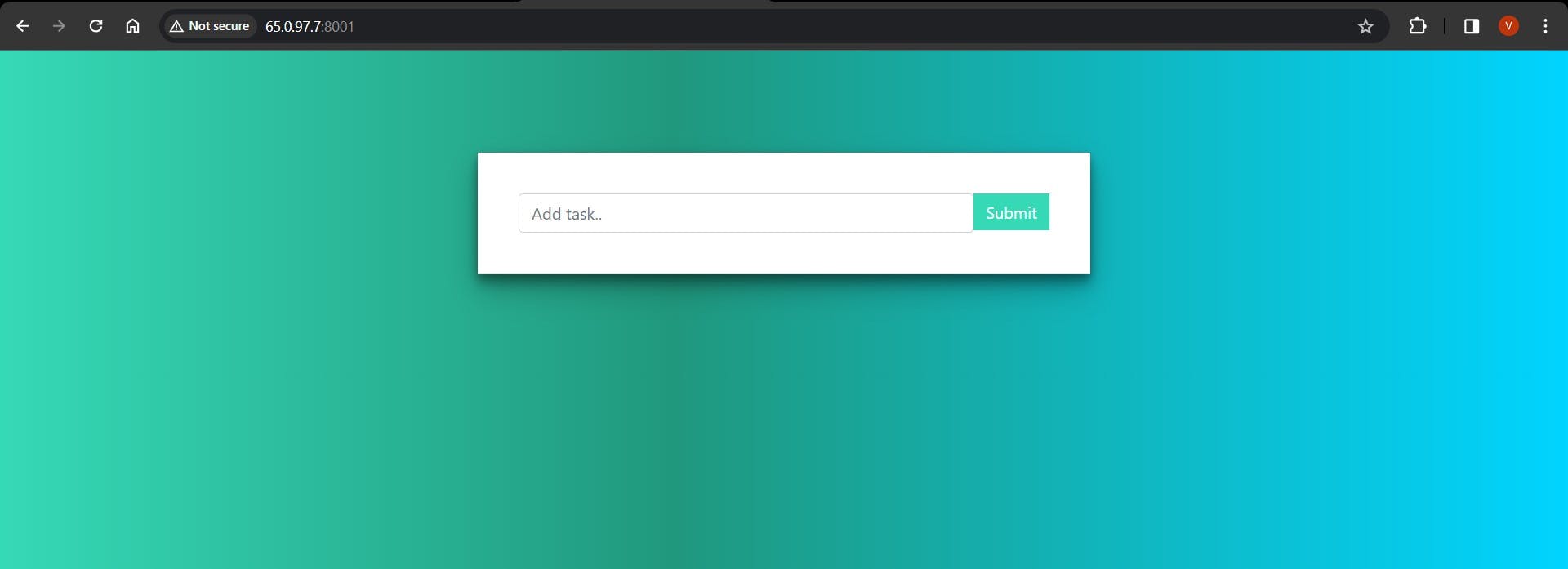
Step 10: Accessing the Web App Access your web application by navigating to the IP address of any node within the swarm followed by port 8001 (e.g., <Any_ip_of_3_vms>:8001).

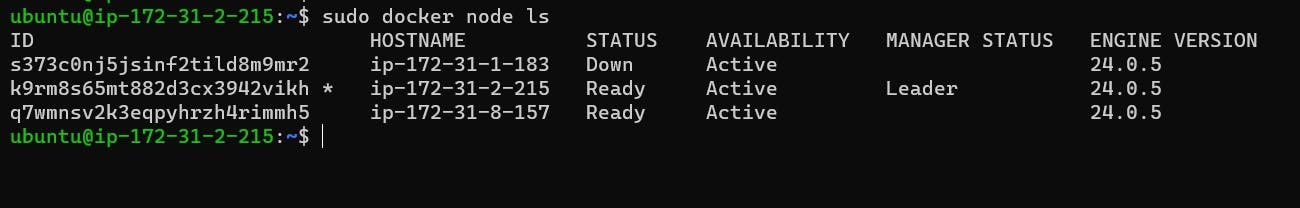
Step 11: Removing Nodes Should the need arise to remove a node from the environment, utilize the command "sudo docker swarm leave" on the respective worker node. Confirm the node's status using "docker node ls".

Conclusion: Project 4 showcases the seamless deployment of a web application using Docker Swarm on AWS, emphasizing scalability, resilience, and efficient management for your applications. Stay connected for more insightful projects and updates.